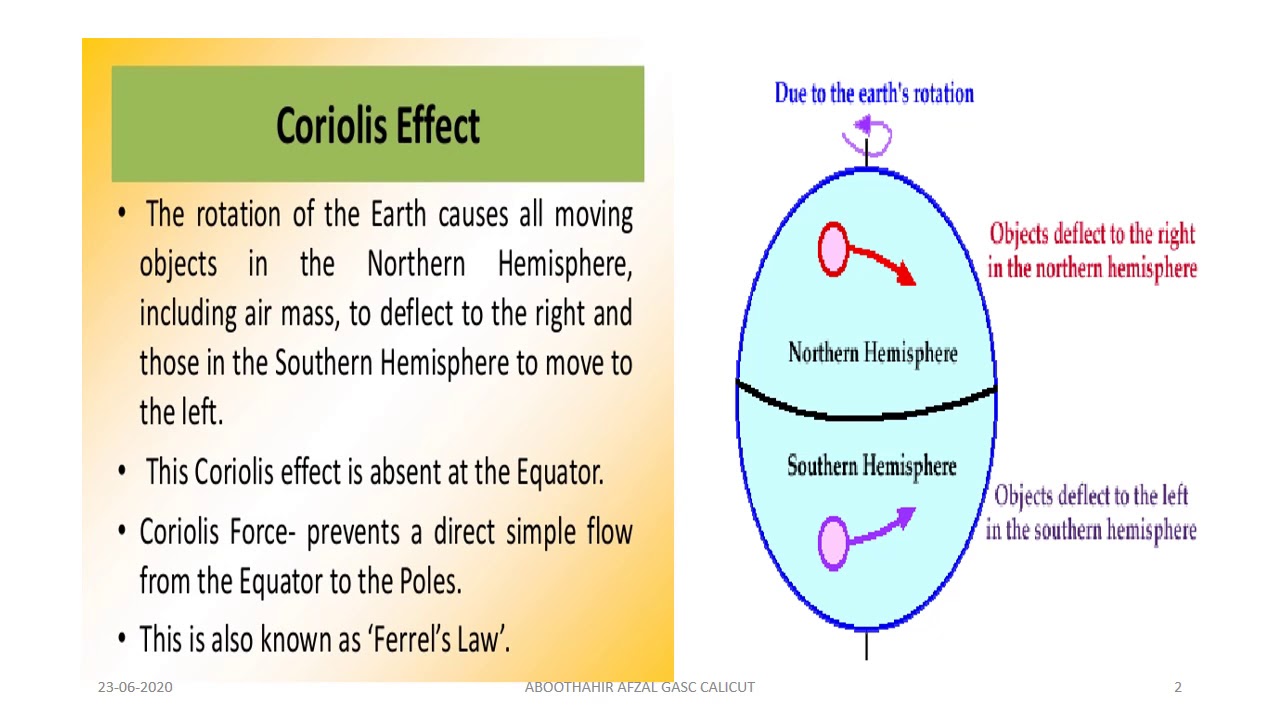
What is the Coriolis Effect? The Coriolis Effect is an apparent effect produced by a rotating frame of reference. The effect occurs when an object moving along a straight path is viewed from a non-fixed frame of reference. The moving frame of reference is the Earth which rotates at a fixed speed. Therefore, when an object moving in a straight.. The Coriolis Effect is so important, in fact, that it influences almost every significant weather event occurring around the world. And it all directly results from the Earth's rotation: The Coriolis Effect is caused by the Earth's rotation from west to east. This causes a deflection in air movement as it travels away from Polar & Equatorial.
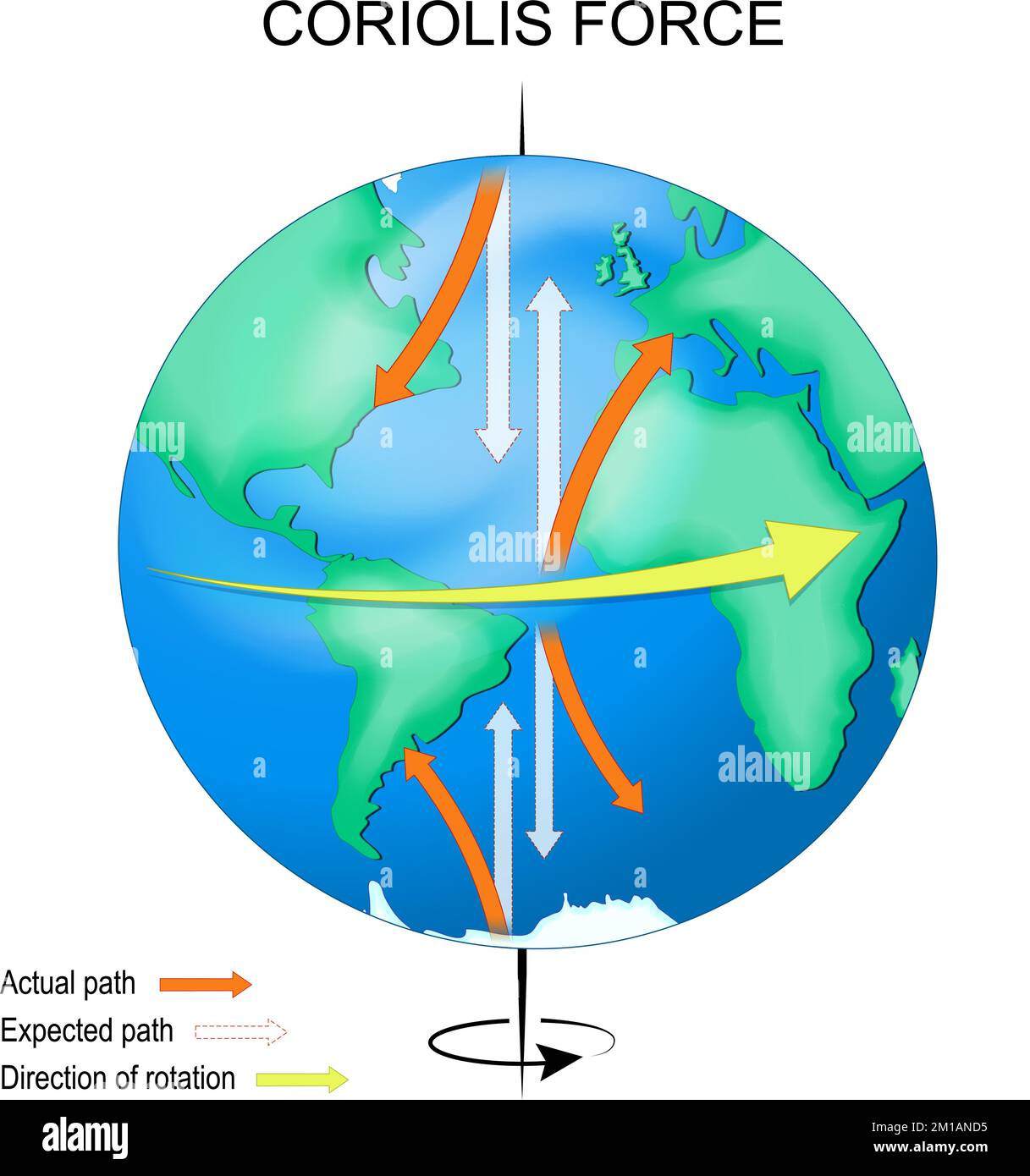
Coriolis effect. Earth with continents, equator, axis and arrows that show direction of rotation

Coriolis Effect FlatEarth.ws

Coriolis Effect

Coriolis force Description, Examples, & Facts Britannica
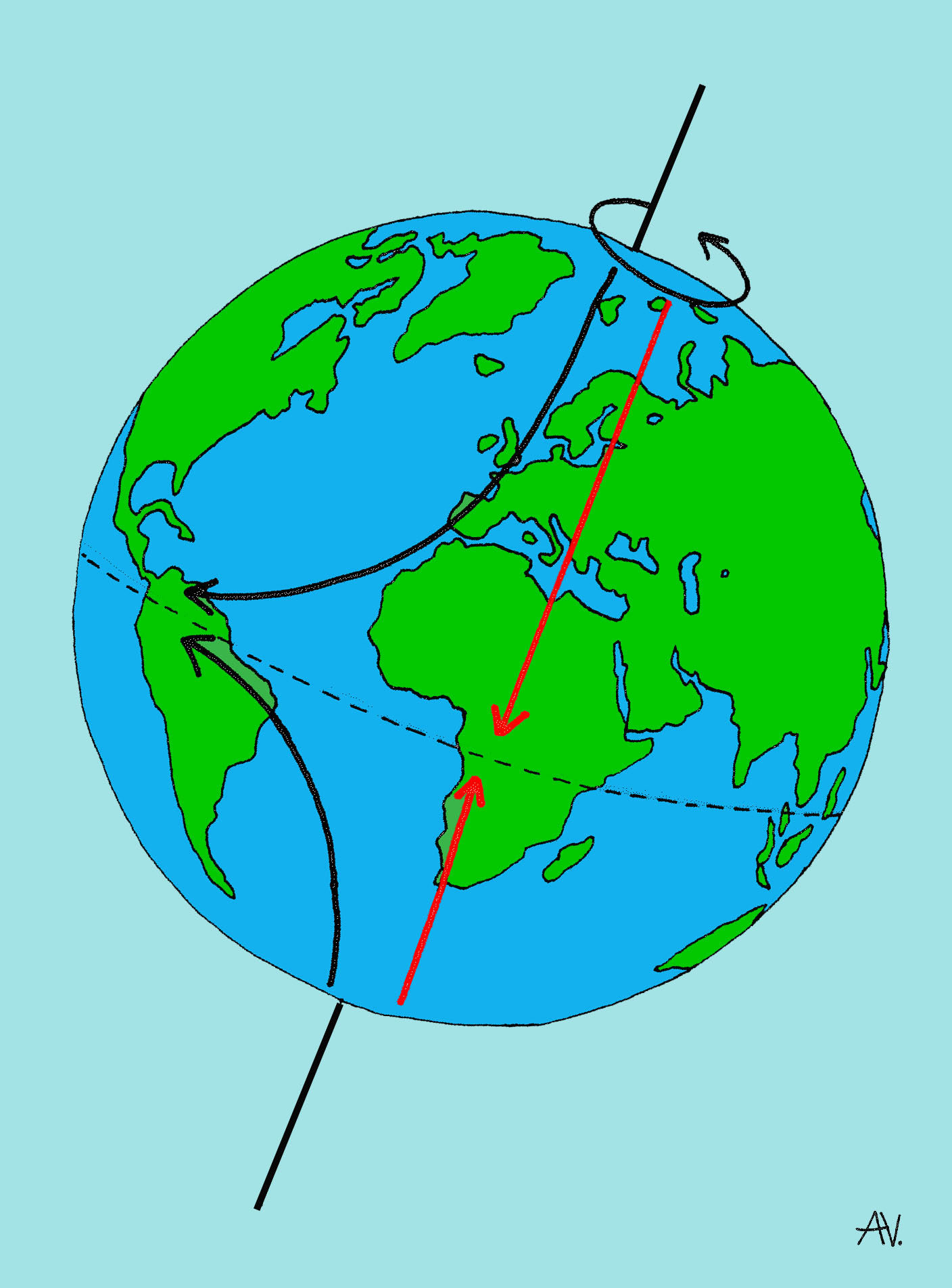
Alles over de plastic soep Wat is het corioliseffect?
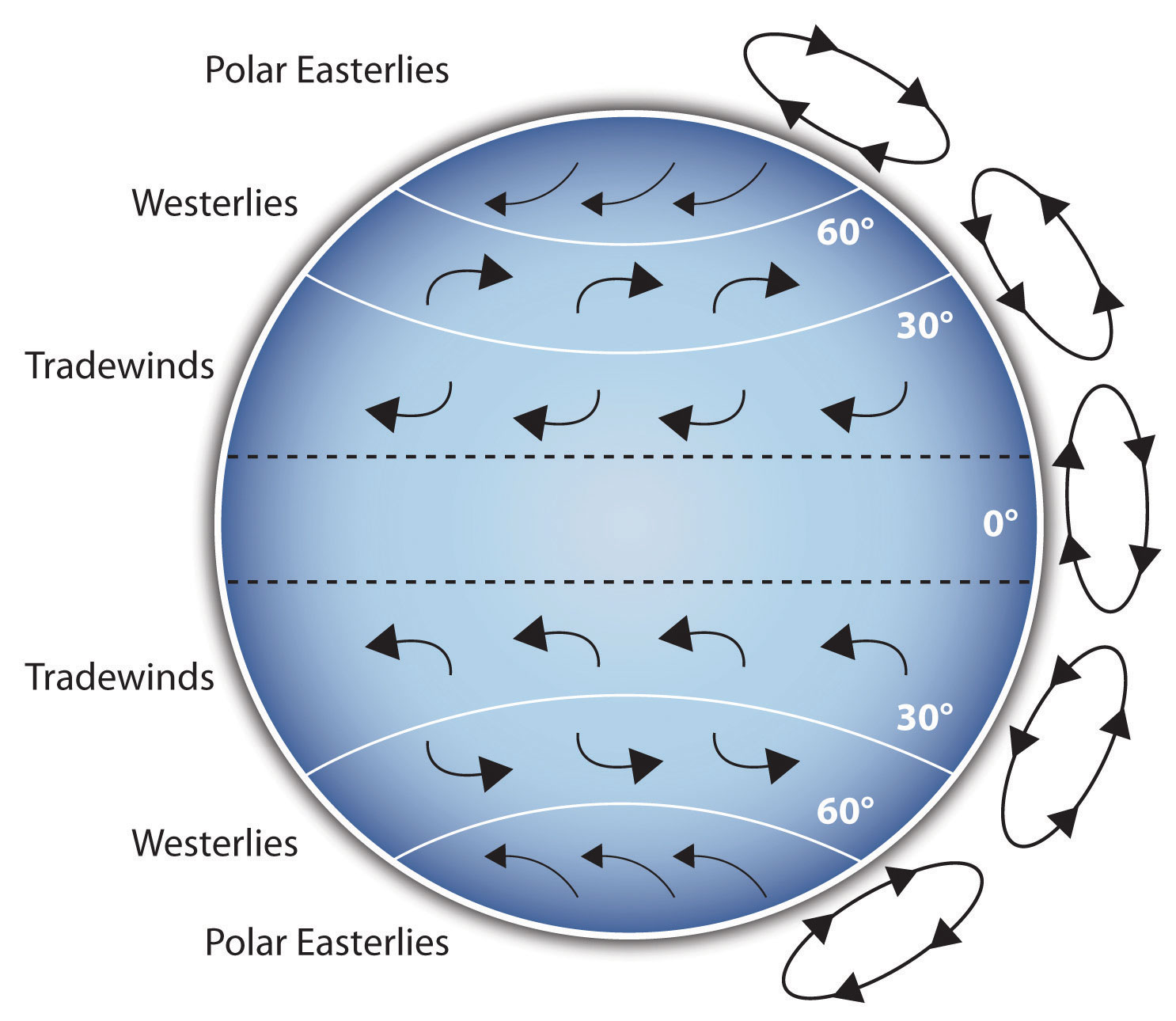
Opinions on Coriolis effect
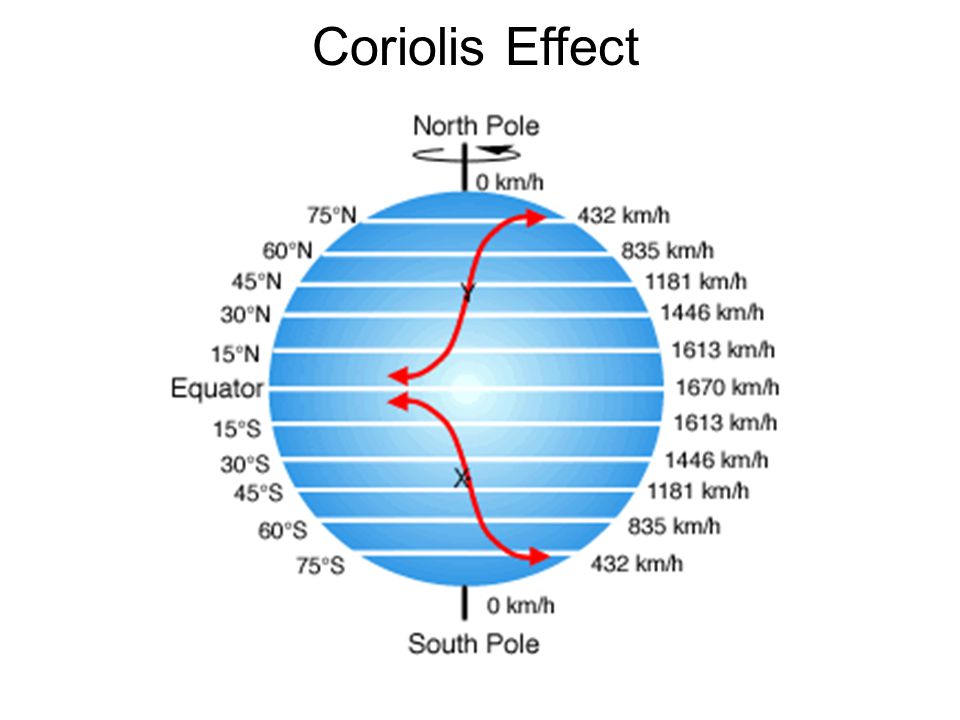
Coriolis Effect. ppt video online download

9.4 Surface Currents Geosciences LibreTexts

The Coriolis Effect Field Notes North Coast Journal

The Coriolis Effect Diagram Quizlet

meteorology Stormstalker
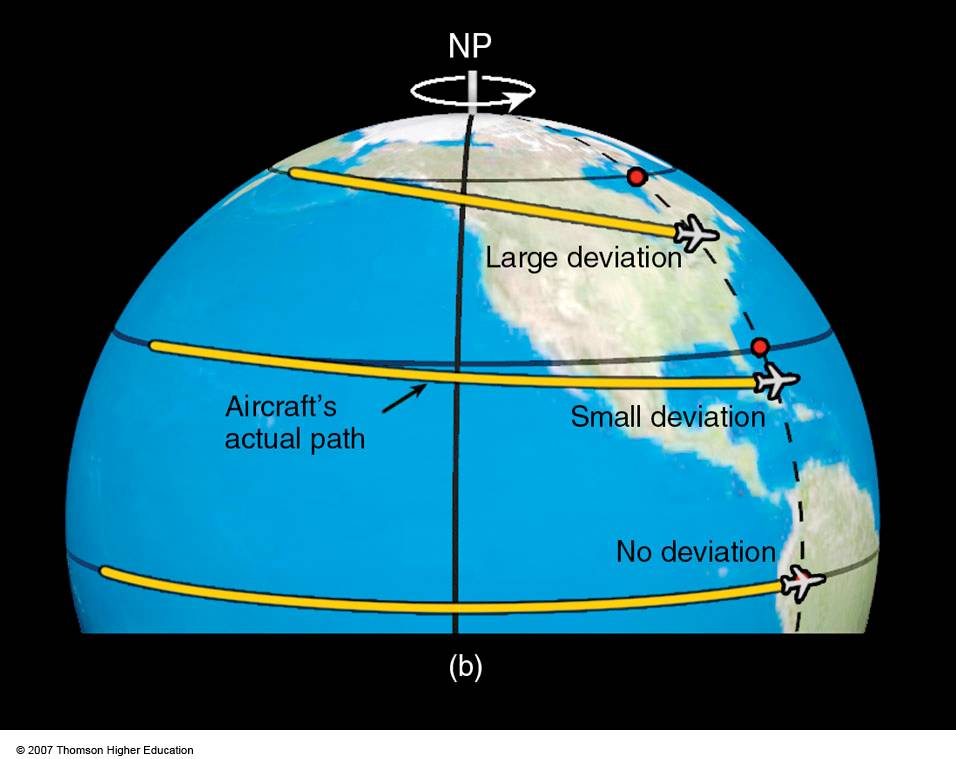
The coriolis force introduction
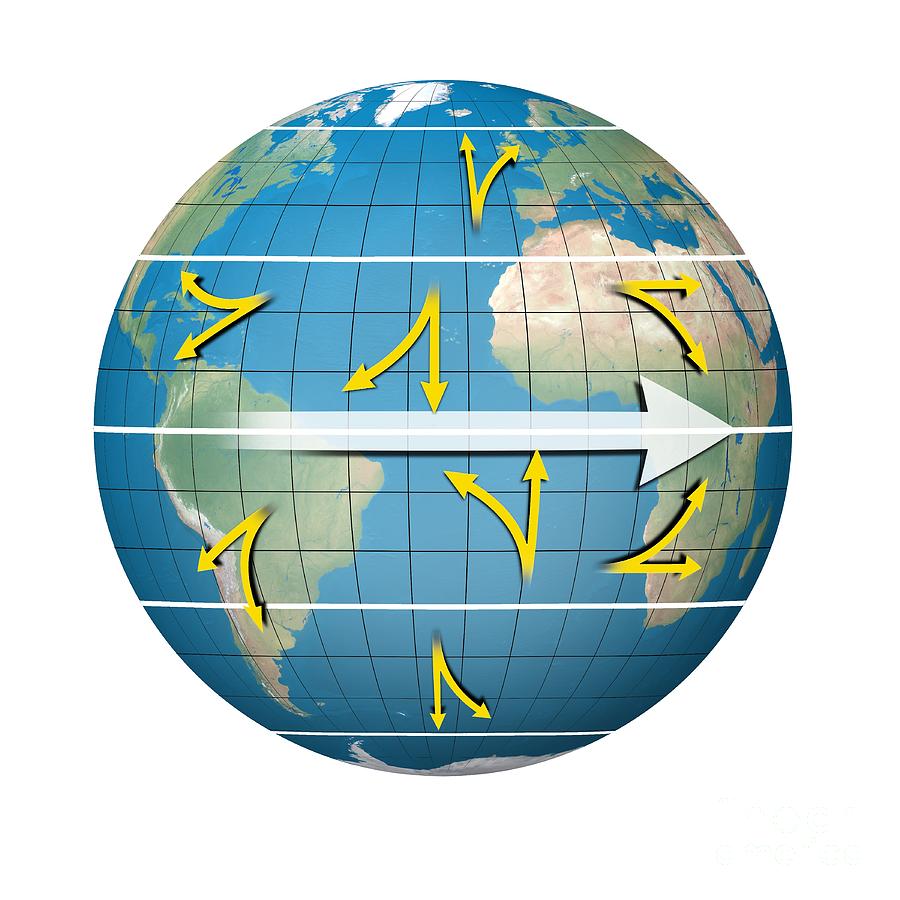
Coriolis Effect, Artwork Photograph by Claus Lunau
Deflection of a falling mass Coriolis effect YouTube
PPT Wind The Coriolis effect PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2608004

What is the Coriolis Effect?

What is the Coriolis force Windy.app
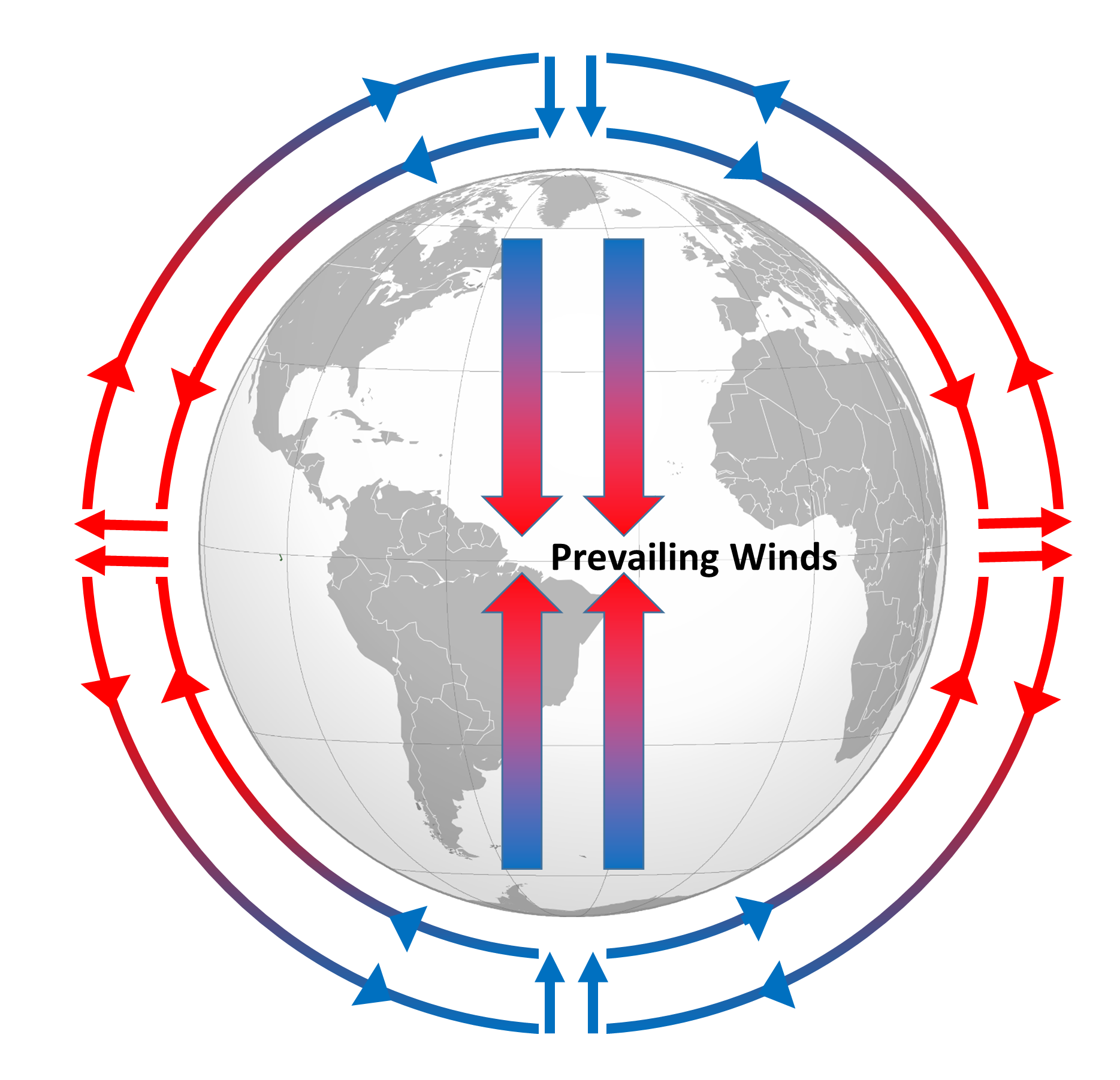
8.2 Winds and the Coriolis Effect Introduction to Oceanography

¿Qué es el Efecto de Coriolis y por qué afecta a tu movimiento? La Runa Arcana
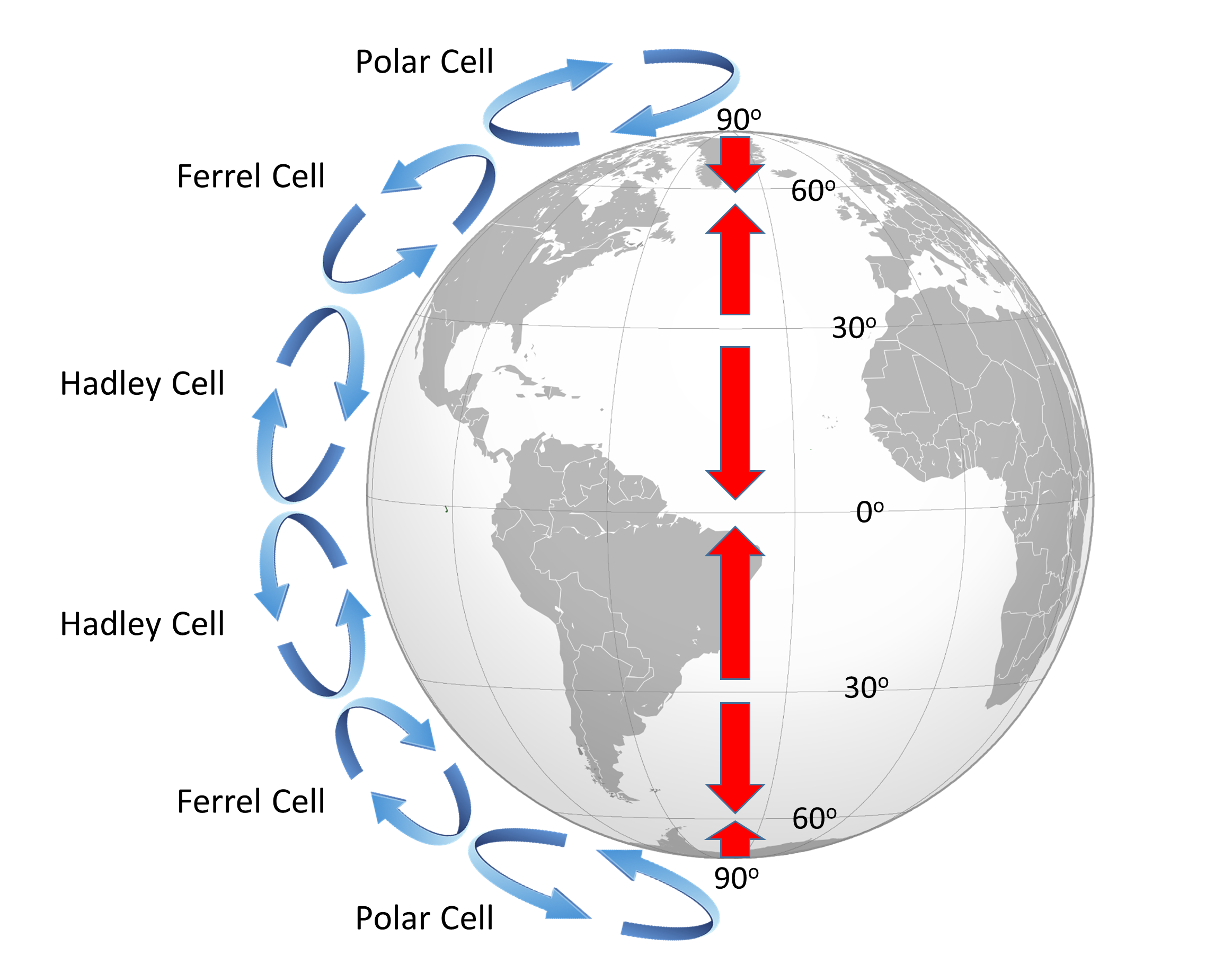
8.2 Winds and the Coriolis Effect Introduction to Oceanography
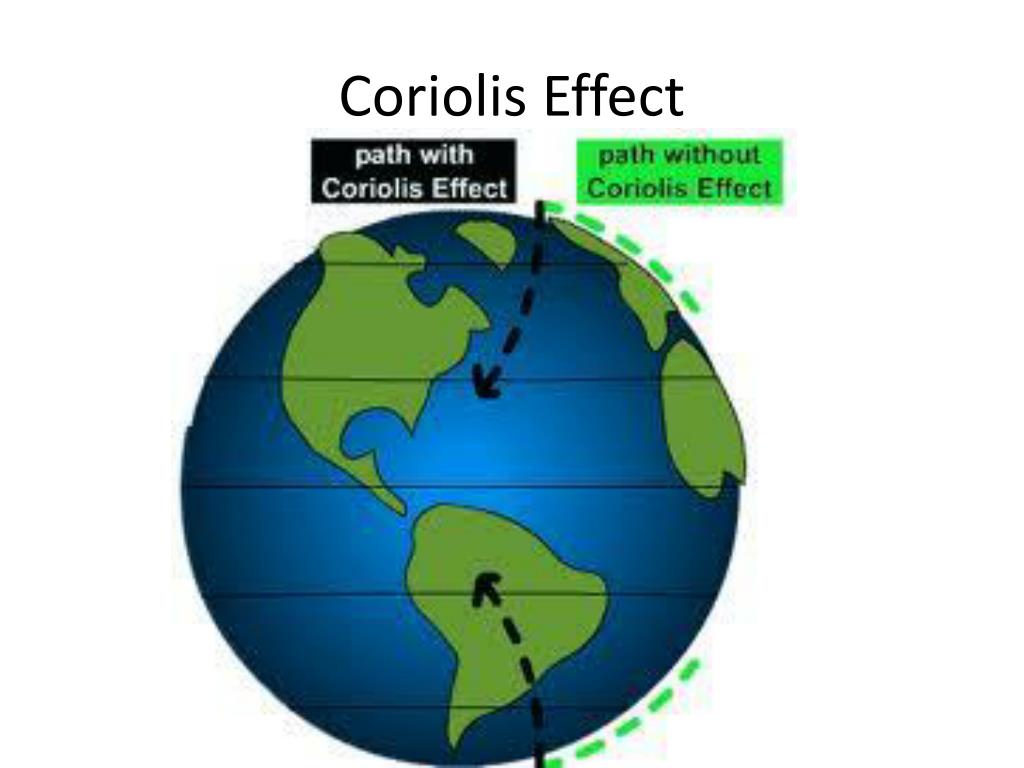
The Coriolis effect can arise in any situation involving rotation. If you stand anywhere on a counterclockwise-turning carousel, for instance, and throw a ball in any direction, you will see the.. The Coriolis effect is responsible for many large-scale weather patterns. The key to the Coriolis effect lies in the planet 's rotation from west to east. Specifically, Earth rotates faster at the Equator than it does at the poles. Every point on Earth takes the same amount of time—24 hours—to make a complete rotation.